Predictive analytics is one of the four main types of data analytics, primarily focusing on predicting future events, such as seasonal sales fluctuations or consumer reactions to price changes. Companies commonly rely on predictive analytics to guide data-driven decisions and enhance results. In this article, we will discuss in detail what predictive analytics is, how it works, and explore its various predictive analytics examples/use cases.
What Are Predictive Analytics?
Predictive analytics is not a new concept & there are lots of predictive analytics examples. It traces back to Henry Ford’s efforts in the late 19th century to analyze data and gain insights for business improvements. Interest in data analytics began to grow during the 1960s with the advent of computers across various industries.
By the late 1990s, the term “business intelligence” became popular. It encompassed multiple data science techniques, including classification, statistics, modeling, data mining, visualization, and analytics. Business intelligence provided software solutions, such as ERP systems, to efficiently organize and process large volumes of data. Its purpose was to offer a structured, comprehensive view of a company’s data, enabling managers and executives to analyze past performance and make informed decisions to enhance future processes.
As per Statista, predictive analytics software is booming, expected to surge from a $5.29 billion market in 2020 to $41.52 billion by 2028, driven by its power to analyze consumer trends and optimize business operations.
How Does Predictive Analytics Work?
All predictive analytics models operate using mathematical models, along with historical and current data. To implement a predictive analytics strategy in your business, you need to follow these steps:
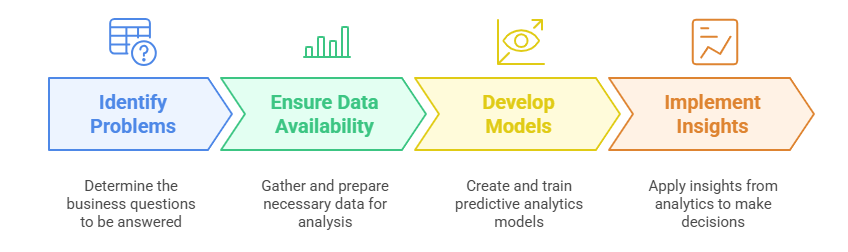
- Identify the problems that need solving. It’s important to have a clear understanding of what you want to discover through data. Ask yourself all the questions you’re looking to answer. For instance, “Which customer groups are most likely to purchase our new product?”
- Ensure you have the required data. For a predictive model to function properly and yield accurate results, it must be provided with sufficient data. For example, to answer the question above, you need detailed information about your customers, such as personal details, purchase history, and brand interactions. The data must be structured, clean, and span a specific timeframe (e.g., one year) so that the analytics model can learn and recognize patterns effectively.
- Develop and train predictive analytics models. You’ll need to build a system using deep learning (DL), machine learning (ML), or artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms that meet your needs. The system should learn from historical data and analyze current data to identify patterns and make predictions. It’s important to regularly retrain the model with updated data, as business environments evolve due to various factors.
- Turn insights into action. Predictive analytics will be effective only if you implement the insights it offers. Therefore, it’s essential to have capable managers who can make strategic decisions based on the predictions provided by the system.
Predictive Analytics Examples/Use Cases
Predictive analytics can be applied in almost any industry to positively influence different business areas. Specifically, companies can:
- Gain deeper insights into customer behavior
- Minimize risks
- Address inefficiencies
- Optimize operations
- Boost productivity
- Drive revenue growth.
Now, let’s explore some common predictive analytics examples in various industries.
1. Retail
Retailers are currently among the top users of predictive analytics. In a fast-paced retail environment, businesses must constantly track customer behavior and market trends to adapt and respond quickly to changes. The significance of predictive analytics in retail is immense. Predictive analytics software assists marketers and retail professionals at every stage of the customer buying journey. Here are some common use cases:
-
- Predictive Marketing: Advanced algorithms analyze market trends, purchasing habits, and customer details to identify buying patterns and segment customers. This enables specialists to optimize marketing campaigns, provide personalized recommendations, and forecast sales, leading to increased revenue and better customer retention.
- Predictive Inventory: Intelligent analytics models assess various factors such as region, season, and purchasing behavior to predict product demand. This allows retailers to maintain optimal inventory levels, preventing both overstocking and stockouts, ensuring they meet customer needs efficiently.
- Predictive Supply Chain: Predictive analytics algorithms enable companies to optimize various elements of their supply chains. First, they enhance logistics by identifying the fastest and most cost-effective routes, taking into account factors like tolls, traffic, and weather conditions. Second, trackers monitor fuel consumption and driver behavior, helping to reduce transportation costs. Lastly, sensors keep track of machine conditions and components, predicting maintenance needs and preventing downtime.
2. Healthcare
A growing number of medical institutions globally are integrating software systems into their operations, allowing them to gather vast amounts of patient data. This opens up numerous opportunities for predictive analytics. By analyzing historical and current data, advanced algorithms can:
-
- Identify early signs of diseases and recommend preventive treatments
- Forecast the outcomes of different treatments and select the most effective option for each patient
- Anticipate disease outbreaks and epidemics
These insights are crucial for enhancing diagnoses and treatments, offering personalized patient care, and ultimately saving lives.
3. Internet of Things (IoT)
Predictive analytics is closely tied to the Internet of Things (IoT), as IoT technology generates vast amounts of data that can be analyzed. A primary use case today is predictive maintenance in smart manufacturing. IoT sensors on machinery continuously monitor performance and send data to processing platforms, where predictive models analyze it, detect anomalies, and recommend maintenance for specific components. This approach helps factories and plants prevent equipment failures and reduce downtime.
4. Sports
Predictive analytics is also becoming increasingly popular in the sports industry. Professional teams in sports like football, baseball, and basketball hire data analysts to evaluate player performance and assist team managers in making optimal contract decisions. Analytics experts assess both on-field and off-field data to predict a player’s value and potential decline. On-field metrics include physical performance factors such as speed, scoring, tactics, and health.
Off-field metrics relate to the business aspect of sports, providing insights into how much profit a player can bring to a team or club. This includes fan engagement, ticket sales, and merchandise revenue, often gathered from sources like social media and ticket vendors.
5. Weather
Over the past decade, weather forecasting has become much more accurate thanks to predictive analytics. Advanced models analyze historical meteorological data along with real-time data from satellites to identify weather patterns and generate precise long-term forecasts.
Weather analytics is crucial not only for daily planning but also for predicting extreme weather conditions such as hurricanes, high winds, or temperature extremes. This allows individuals and municipal services to prepare in advance, helping to mitigate significant damage or loss.
6. Insurance
In the insurance industry, managing risk is at the core of operations, making predictive analytics an invaluable tool. Advanced algorithms streamline the insurance claim approval process by analyzing previous claims and identifying potential risk factors. What might take weeks to review manually can be completed automatically and instantly with predictive analytics. This allows insurance companies to better estimate future risks, detect fraudulent claims early, and reject them, thereby minimizing unnecessary costs.
7. Financial Modeling
Financial planning is crucial for businesses across all sectors. Many finance teams are already leveraging predictive analytics, or plan to, to anticipate risks and forecast revenue. Predictive models help allocate resources effectively, optimize operations, and prevent additional expenses. Numerous financial management software solutions now include predictive analytics features, signaling the growing importance of intelligent algorithms in financial services.
8. Social Media Analysis
For most brands today, maintaining a presence on social media is essential, as it serves as the primary platform for customer interaction. The data generated from social media channels is highly valuable to businesses when properly analyzed. Predictive analytics tools enable companies to extract meaningful insights from customer comments, reviews, likes, dislikes, and discussions, allowing them to make adjustments to their business strategies accordingly.
9. Energy
With the rise of electric vehicles and renewable energy, global electricity consumption will continue to grow, requiring the energy sector to scale production to meet this increased demand. Predictive analytics plays a vital role by helping energy providers forecast both short- and long-term energy demand, taking into account factors like weather conditions, seasonality, and new consumers. Additionally, predictive maintenance minimizes equipment failures, reducing unexpected costs and ensuring a more stable energy supply for customers.
10. Human Resources
HR departments manage vast amounts of employee data, making predictive analytics an effective tool for optimizing processes. HR professionals can use it to predict employee performance, staff turnover rates, and the impact of activities on employee engagement. By analyzing this data, companies can identify problem areas in human resource management and make data-driven decisions for better workforce allocation. This ultimately leads to improved employee satisfaction and higher productivity.
Conclusion
These predictive analytics examples are enough to conclude that without smart business operations software, the value of your data is limited. However, with an effective operations management platform, you can oversee all inputs, events, and data that offer real-time insights into your business. By incorporating predictive analytics, you can shift from merely reactive operations to proactive and predictive strategies, allowing you to plan for the future and discover new business opportunities.
Are you considering incorporating the latest technology into your business operations? As a leader in software development services, Intelegain prioritizes innovation and client satisfaction. This enables you to provide customizable and scalable solutions across various industries. Contact us for FREE consultation on how you can leverage predictive analytics to transform your business operations.
FAQs
1. How do companies perform predictive analysis?
Predictive analysis involves gathering and preparing data, choosing suitable modeling techniques, training models, and assessing their accuracy. Companies use various software tools and platforms to execute this process based on their unique requirements and objectives.
2. Why is predictive analytics crucial in finance?
Predictive analytics plays a vital role in finance by helping to predict future financial trends, reduce risks, and support data-driven decision-making for better outcomes.
3. What are the key components of predictive analytics?
The core components of predictive analytics are data collection, data processing, and predictive modeling, which together create the basis for generating insights.
4. What is the most commonly used technique in predictive analytics?
Regression analysis is the most frequently employed technique in predictive analytics, used to forecast numerical results by identifying relationships between variables.










